Kieferorthopädie Wien – Zahnspange
Mon-Fri : 10am – 5pm
Braces for Children, Early Treatment in Primary and Mixed Dentition.
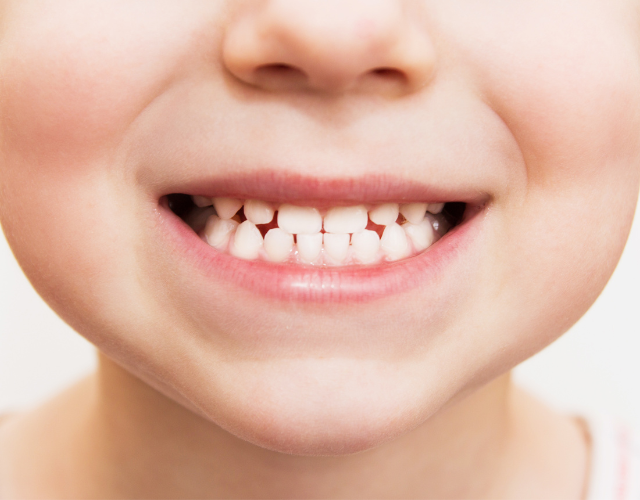

Braces for children
- Alternativen -
Orthodontic or teeth straightening treatment in the primary teeth is usually only necessary if the teeth are misaligned in children between the ages of 6-10.
Braces for children, the diagnosis and the right timing is very important.
- The right time is crucial : to make optimal use of facial skull growth, tooth change and tooth eruption for treatment.
- After the treatment, the active phase of therapy, the important one takes place Retention phase to stabilize the treatment result.
- Sometimes treatment in two phases makes sense.
- In phase 1, jaw or tooth misalignments (e.g. growth-dependent misalignment) or anomalies are corrected with removable devices in the primary teeth, in the early mixed dentition.
Growth is essential for optimal treatment of the misalignment (lower jaw retention, upper jaw retention). - Phase 2: from the age of 12, when children lose milk teeth.
- In phase 1, jaw or tooth misalignments (e.g. growth-dependent misalignment) or anomalies are corrected with removable devices in the primary teeth, in the early mixed dentition.
- Unfavorable growth can influences or worsen the misalignment and are sometimes the reason why orthodontic prognoses are negatively influenced.
- Prognathism refers to a jaw misalignment that is characterized by a reversed overbite of the incisors (frontal crossbite) as the main symptom.
- Skeletal developments are of great importance for the timing of orthodontic therapy.
- At extremes Dysgnathias(Summary of maldevelopment of the teeth, jaws and/or the chewing system) attempts should be made to counteract unfavorable development through preventive or early therapeutic measures.
Exact Time to start or check for Orthodontic treatment:
As a rule, the first phase of treatment begins from the age of 6-10 – early treatment. This treatment is necessary in order to be able to treat the misalignment in primary or mixed teeth.
Does your child need braces? Here is the typical procedure of treatment:
- Free initial consultation for misaligned teeth in our orthodontics. Appointment only by appointment!
- Create treatment documents for individual treatment courses. Diagnosis with x-rays, photos and digital scans. Always without marks.
- Plan discussion and explanation. X-ray evaluation and the analysis discussion about which type of braces and/or brackets are necessary for the individual case.
- Start of treatment. Inserting the device and providing information about cleaning and wearing times
- Important and necessary check-ups every 6-8 weeks
- End of treatment. Removing the braces and discussing the results of the treatment
- Retention– the beginning of stabilization of the treatment result.
Here you will find the entire process in my orthodontics explained in detail.
Examples: Children who need orthodontics/tooth straightening:
Placeholder
Fixed space maintainer: If children lose milk teeth early, space must be kept for the teeth that will follow.
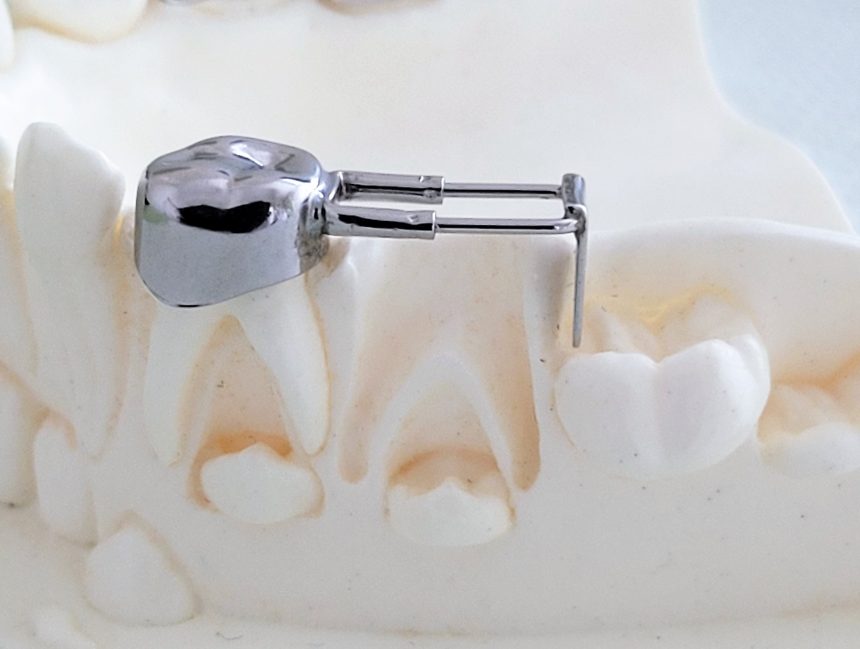
Crowding-less space in jaw
Primary crowding: is hereditary, a mismatch between jaw size and tooth size, either the teeth are too big or the jaw is too small.
Secondary crowding : is acquired and occurs due to early loss of primary teeth.
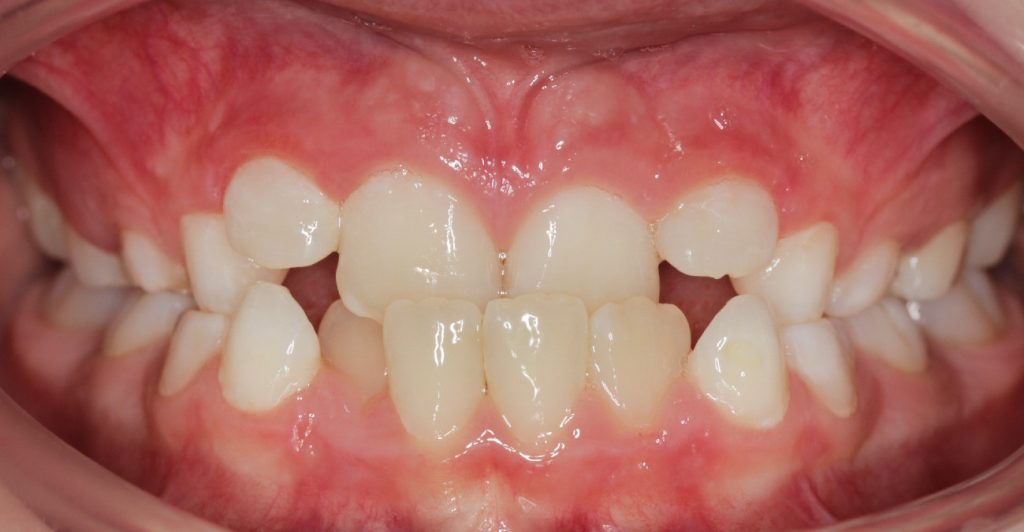
Traumatic deep bite-overbite
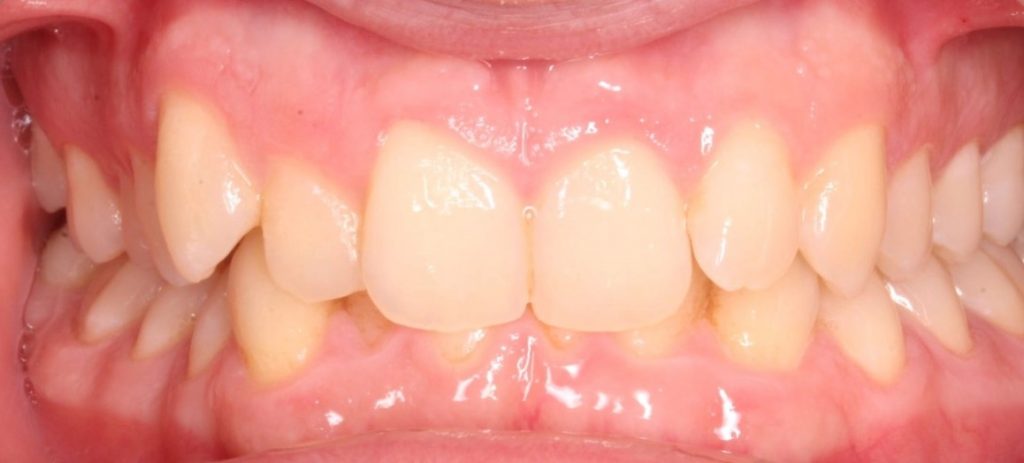
Lateral crossbite
Lateral crossbite with risk of growth inhibition of the upper jaw
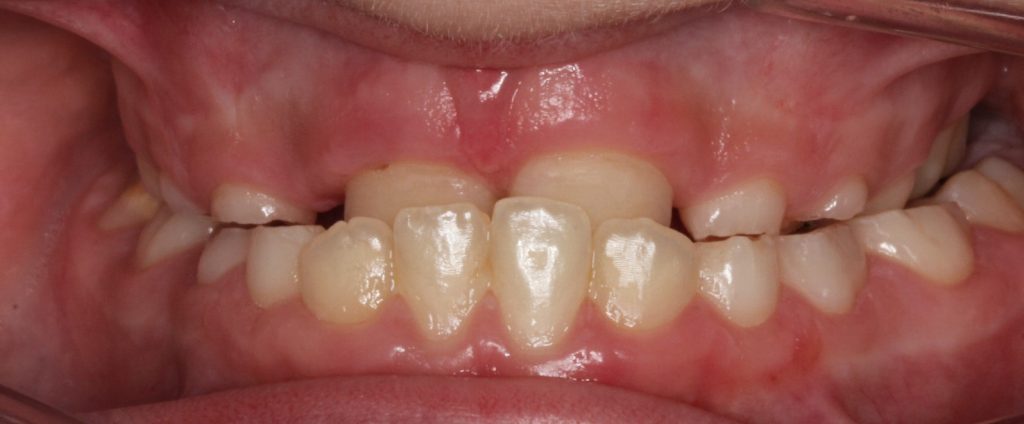
Upper jaw reduced growth
KL 3-growth inhibition in the upper jaw or excessive growth in lower jaw.

Primary dentition prognathism-anterior crossbite
Reduced growth in upper jaw, KL 3 growth inhibition in the upper jaw


Dr.med.dent Manish Sablania M.Sc.Orthodontics
Dr.med.dent Manish Sablania BDS M.Sc. Specialized Orthodontics-Dentist Vienna 1200
- Qualified orthodontist for “health insurance – free braces“ specialized in orthodontics and orthodontics.
- Has over 23 years of experience and more than 6500 dental adjustments and braces treatments, cooperation , which makes him an expert in his field who cares deeply about the well-being of his patients.

